laboratory analysis meaning|what is assay in chemistry : dealers LABORATORY ANALYSIS definition | Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples São Paulo Testemunhas de Jeová. Resumen en portugués. Esse trabalho tem como objetivo analisar a ação das Testemunhas de Jeová, seita religiosa milenarista norte-americana, em São Paulo, entre os anos de 1930 e 1954. Em meio aos governos de Vargas e Dutra, à Segunda Guerra Mundial e ao início da Guerra Fria, a "Sociedade .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Sobre os Lagged Jogos De Yad. Aproveite um dos nossos 62 jogos de yad grátis online que podem ser jogados em qualquer dispositivo. Lagged.com.br é a casa de alguns .
LABORATORY ANALYSIS definition | Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examplesLABORATORY ANALYSIS meaning | Definition, pronunciation, translations .3 meanings: → See laboratory 1. a. a building or room equipped for .Laboratory analysis means the original test result for each analysis that was used to determine a product’s properties. For laboratories using test methods that must be .
Laboratory analysis refers to the systematic examination and evaluation of samples, often conducted in controlled environments, to determine their chemical, physical, or biological .
Chemical analysis, chemistry, determination of the physical properties or chemical composition of samples of matter. A large body of systematic procedures intended for these purposes has been continuously evolving in .
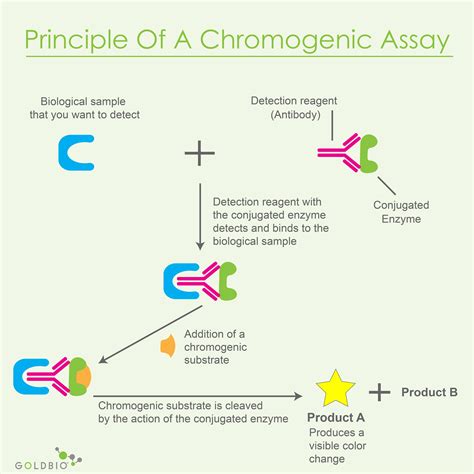
Definition: An assay is a laboratory technique used to measure, analyze, or detect the presence, quantity, or activity of a substance within a sample. Types: Assays come in various forms, including biochemical, .
From risk assessment to risk analysis, evaluation, and control to continuous quality improvement, the clinical laboratory should be able to minimize errors along its path of the .The meaning of LABORATORY is a place equipped for experimental study in a science or for testing and analysis; broadly : a place providing opportunity for experimentation, observation, .
Many different tests exist to detect and measure almost any type of chemical component in blood or urine. Components may include blood glucose, electrolytes, enzymes, hormones, lipids . Laboratory tests check a sample of your blood, urine, or body tissues. A technician or your doctor analyzes the test samples to see if your results fall within the normal range. The tests use a range because what is .
INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF LABORATORY DATA ALFRED A. BARTOLUCCI UniversityofAlabamaatBirmingham Birmingham,Alabama,USA KARAN P. SINGH .
Laboratory methods are based on established scientific principles involving biology, chemistry, and physics, and encompass all aspects of the clinical laboratory from testing the amount of cholesterol in your blood to analyzing your DNA to growing microscopic organisms that may be causing an infection. As defined by PAMA, the PLA code section was developed to include ADLTs and clinical diagnostic laboratory tests (CDLTs) for procedures based on human gene analysis. Recently, however, the language describing . Laboratory tests check a sample of your blood, urine, or body tissues. A technician or your doctor analyzes the test samples to see if your results fall within the normal range. The tests use a range because what is normal differs from person to person.
LAB ANALYSIS definition | Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examplesPopularity of “The Laboratory”: This poem is a classic and dramatic monologue written by Robert Browning, a popular English poet. It appeared in 1845 in his book, Dramatic Romances, and Lyrics.The poem unfolds extreme jealousy of a lady for another woman. It shows how her hatred made her reach a level where she intends to kill her lover’s new girlfriend mercilessly. Definition: An assay is a laboratory technique used to measure, analyze, or detect the presence, quantity, or activity of a substance within a sample. Types: Assays come in various forms, including biochemical, immunoassays, cell-based, molecular, chemical, microbiological, radiometric, and more. Applications: Assays are employed in diverse fields .
The Schuster Laboratory, University of Manchester (a physics laboratory). A laboratory (UK: / l ə ˈ b ɒr ə t ər i /; US: / ˈ l æ b r ə t ɔːr i /; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities . –DL/LOD determined in laboratory water matrix is a lowest possible value –Spikes at the LOD in the matrix of concern may be helpful in understanding your data quality and needs •Limits are adjusted with dilution of sample –i.e., if an analysis with a LOD of 2 is performed on a sample that has been diluted 3x, the LOD for that sample is 6. Name and address of the laboratory location where the test was performed. Tests may be run in a physician office laboratory, a laboratory located in a clinic or hospital, and/or samples may be sent to a reference laboratory for analysis. Date report printed. This is the date this copy of the report was printed.This fact sheet outlines some of the major parameters you may see on the analysis and assists y ou in understanding the report. *** ANALYTICAL LABORATORY REPORT *** Client: Client's name Project: Analytical Laboratory Services Date Collected: 08/28/90 Sample Identification: Kitchen Tap Collected by: KM Project Number: CL000001 Time Collected: 7 .
What Are the Different Types of Laboratory Tests? Clinical chemistry uses chemical processes to measure levels of chemical components in body fluids and tissues. The most common specimens used in clinical chemistry are blood and urine. Laboratory medicine service in a hospital is concerned with relevant investigations of patient’s presenting complaints and sometimes with detection and potential prevention of disease. It involves a systematic approach of clinical advice or request for a particular investigation, analysis of the collected specimen, interpretation of results, and .The blood sample is saved on a special strip of paper that’s sent to a lab for analysis. Heel stick: All babies born in the U.S. have blood tests by pricking their heel with a needle to obtain a blood sample. Arterial blood gas test: In this test, providers take blood from one of .Clinical laboratory in a hospital setting showing several automated analysers.. A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. [1] Clinical medical laboratories are an example of applied science, as .
In every scientific laboratory, there is a set of fundamental skills that needs to be mastered. A solid foundation of core lab skills is essential to produce accurate, reproducible results, as well as to prevent damaging . A lab report conveys the aim, methods, results, and conclusions of a scientific experiment. . materials, and specific procedures used for data collection and analysis. Experimental design. Briefly note whether your experiment is a within-subjects or between-subjects design, and describe . The mean heights of the plants in the control group .
Crime laboratory, facility where analyses are performed on evidence generated by crimes or, sometimes, civil infractions. Crime laboratories can investigate physical, chemical, biological, or digital evidence and often employ specialists in a variety of disciplines, including behavioral forensic . though that type of analysis is often grouped .
Bacteria in your urinary tract can create nitrites. A positive nitrite test result can mean you have a UTI. Protein. This measures the presence of proteins, like albumin, in your pee. . If the lab finds red or white blood cells, bacteria, yeast or other countable substances, the results might be listed as “few,” “moderate” or “many The practical meaning of LOQ is that LOQ is the lowest concentration that can be measured with an accuracy of about ±30%; AIHA LAP uses the term RL (reporting limit) which is LOD times a safety factor selected by the laboratory. RL is selected high enough to ensure that day-to-day variation in laboratory instrument sensitivity does not exceed .What do the results mean? A CSF analysis may include a variety of different tests on your sample. So, the measurements on your test results will depend on which tests were done. . Hinkle J, Cheever K. Brunner & Suddarth's Handbook of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. 2nd Ed, Kindle. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams .Definition of laboratory noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more. . to send a specimen to the laboratory for analysis; in a/the laboratory The effects of weathering can be simulated in the laboratory.
Analytical quality control (AQC) refers to all those processes and procedures designed to ensure that the results of laboratory analysis are consistent, comparable, accurate and within specified limits of precision. [1] Constituents submitted to the analytical laboratory must be accurately described to avoid faulty interpretations, approximations, or incorrect results. [2]Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) combines the easy sample introduction and quick analysis of ICP technology with the accurate and low detection limits of a mass spectrometer. This ICP analysis method exhibits high sensitivity and can perform multi-element analysis, often at the parts-per-trillion level.Pre-laboratory phase is a better term as it highlights that this phase is beyond the direct control of the laboratory and pathologists, and needs coordination and cooperation of many departments and individuals, such as clinicians, nurses, porters, medical assistants, various departments – medical, surgical, information technology, emergency .
A certificate of analysis (COA) is a formal laboratory-prepared document that details the results of (and sometimes the specifications and analytical methods for) one or more laboratory analyses, signed—manually or electronically—by an authorized representative of the entity conducting the analyses. This document gives assurances to the recipient that the analyzed . Let’s try another example. A medical laboratory scientist must dilute a specimen times 10 (x10) with normal saline prior to using it for analysis to ensure the analyte in the specimen is at the proper ratio to interact with the reagent optimally. (Oh, no!
soil permeability test 50 ml of water
WEBAre you looking for a new and exciting way to play online games? If so, you should check out game.today777.com, a subdomain of Today777 that offers exclusive access to .
laboratory analysis meaning|what is assay in chemistry